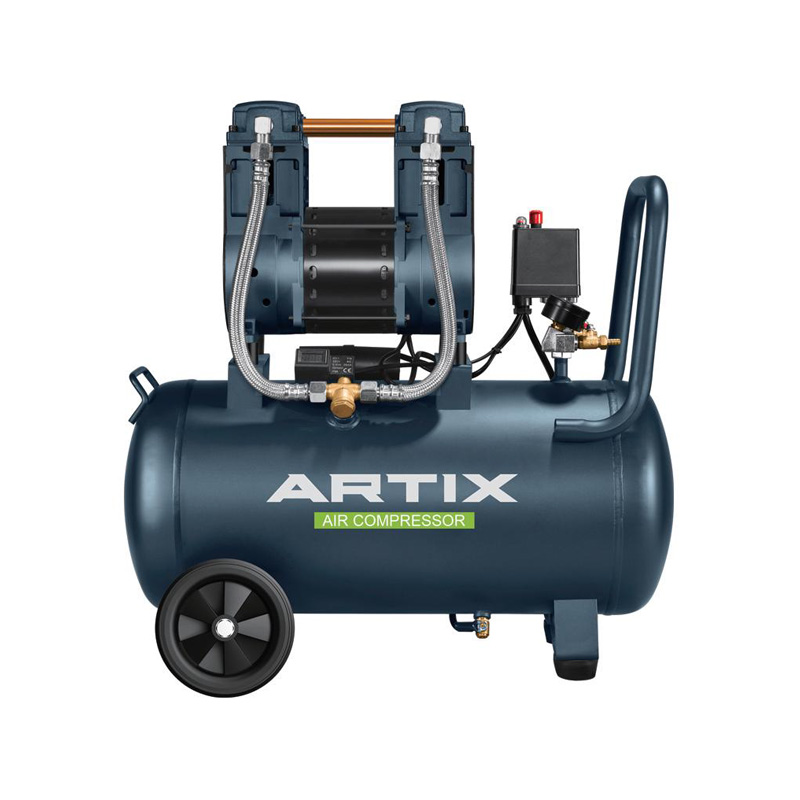
High-demand settings, such as manufacturing facilities, automotive workshops, and construction sites, place significant stress on air compressors, which must be optimized to prevent downtime and reduce operational costs. This article explores strategies for enhancing the performance of electric-driven compressors, high air compressors, and 12L air compressors to meet demanding requirements.
1. Understand the Needs of Your High-Demand Setting
Before selecting and configuring an air compressor, assess the specific requirements of your operational environment. In high-demand settings, air compressors are frequently used for extended hours, sometimes around the clock. Electric-driven compressors are ideal for these situations as they offer steady, reliable power without the fluctuations associated with fuel-driven models. When paired with the correct setup, these compressors can handle prolonged tasks without overheating or malfunctioning.
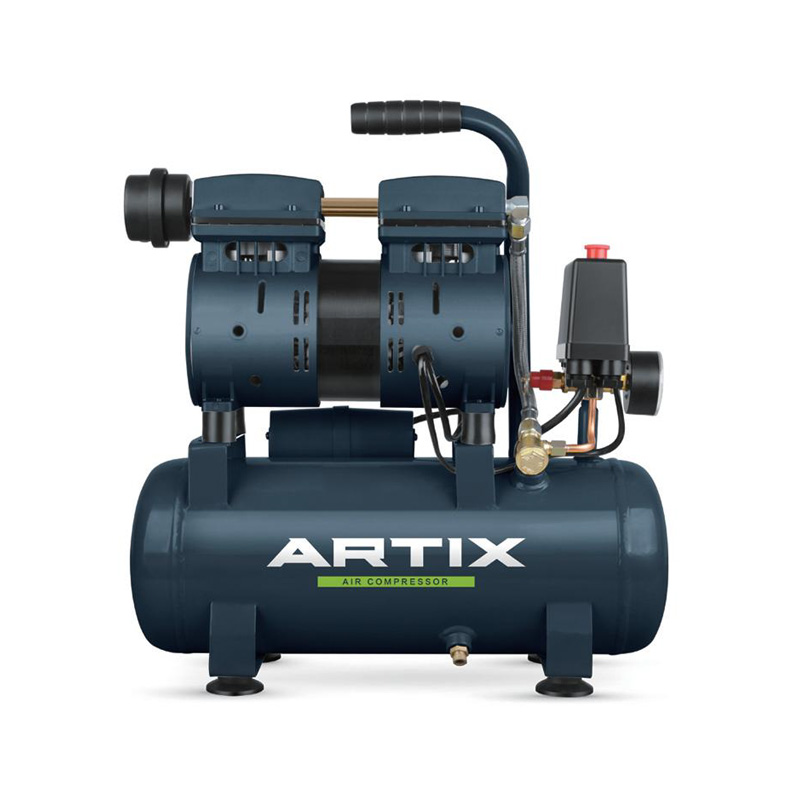
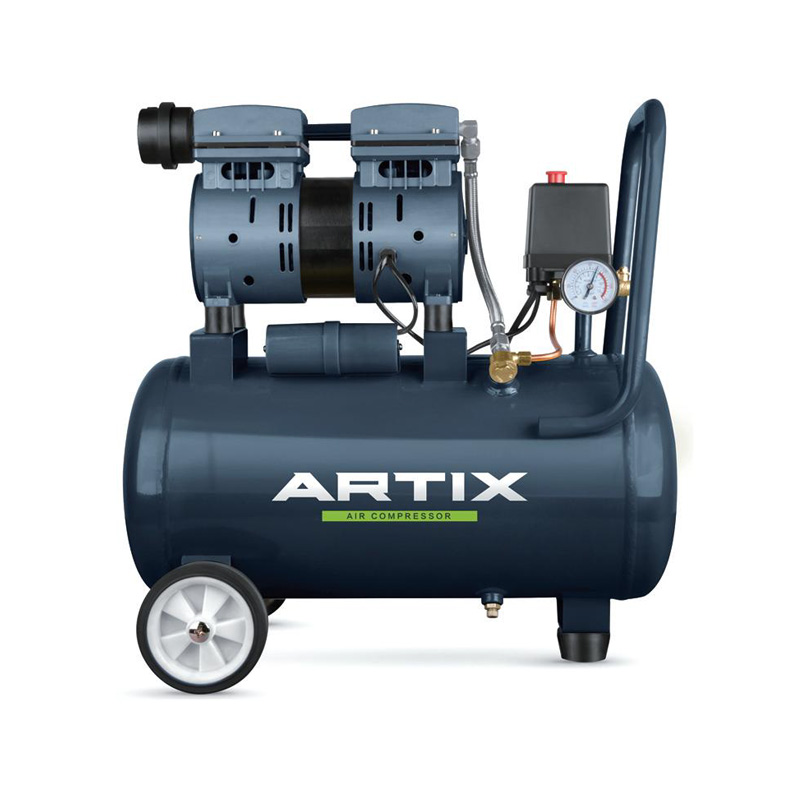
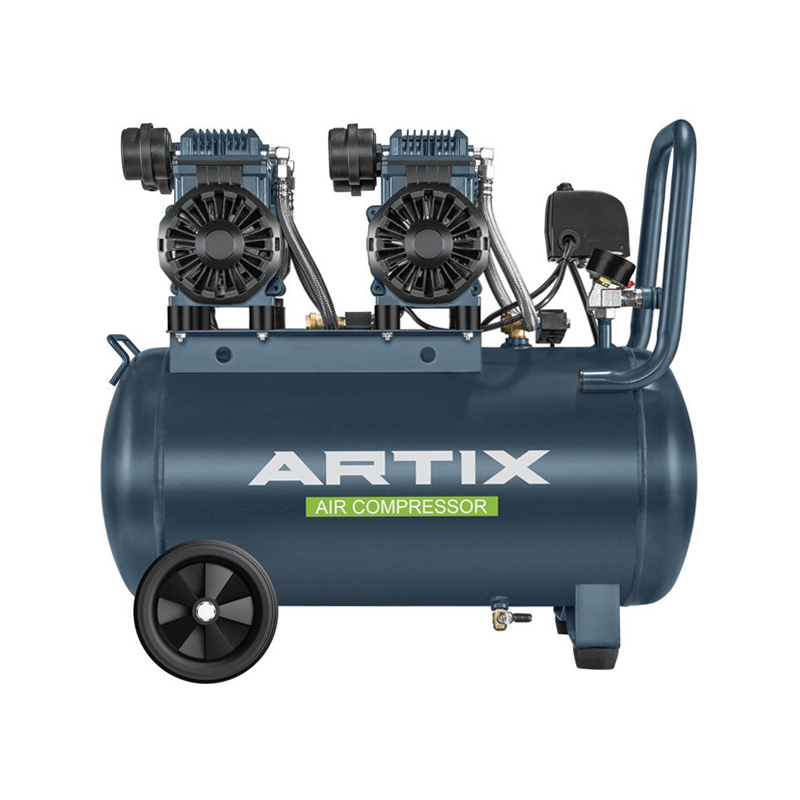
Additionally, when determining the appropriate size, a high air compressor with adequate air pressure capacity is essential for environments requiring powerful, consistent airflow. For smaller yet high-performing tasks, a 12L air compressor may be suitable, especially when portability is required. Understanding these specifications will help in choosing the right equipment to avoid frequent replacements and repairs, improving both productivity and cost-efficiency.
2. Regular Maintenance and Inspection
Proper maintenance is fundamental in optimizing air compressor performance. Components such as filters, valves, and belts experience wear and tear faster in high-demand settings. Without consistent inspection and maintenance, these components may fail, pilot to unexpected downtime.
For electric-driven compressors, inspect electrical connections and wiring periodically to prevent electrical faults. High-air compressors should also have filters cleaned or replaced regularly to avoid clogging, which can restrict airflow and put additional strain on the motor. For 12L air compressors, the small tank size means it cycles more frequently in demanding tasks; therefore, checking for leaks and ensuring all seals are intact is essential.
Maintaining a logbook for each compressor, noting every service, repair, and inspection, can assist in identifying patterns that indicate when specific parts may need replacing. This proactive approach can prevent costly repairs and downtime, ensuring consistent performance.
3. Monitor Air Pressure and Avoid Overloading
High-air compressors are designed to deliver strong, consistent pressure, but overloading them beyond their rated capacity can cause premature wear. Each compressor has an up-to-pressure rating, and exceeding it can advance to motor burnout or tank rupture. Operators should check the pressure settings and ensure that they do not exceed the compressor’s rated capacity.
For electric-driven compressors, overload issues can sometimes be mitigated by distributing workloads across multiple machines if possible, especially during peak operational hours. Similarly, for 12L air compressors, given their compact design, it’s important to avoid high-demand tasks that exceed the tank’s capacity to maintain longer operational life.
Pressure control mechanisms, like regulators, can be adjusted based on the specific tasks performed. If your work requires varying pressure levels, consider setting different ranges for different tasks to keep the compressor within safe limits. This strategy will help prevent equipment damage and optimize energy consumption.
4. Utilize an Efficient Layout for Air Distribution
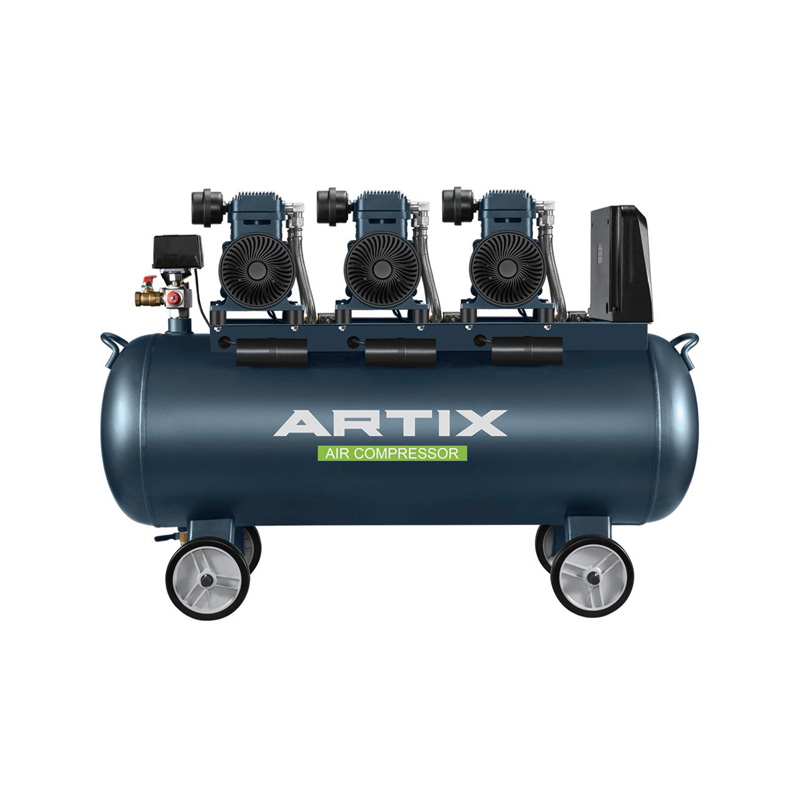
In many facilities, multiple air-powered tools rely on a central compressor system. By planning an efficient air distribution layout, businesses can less pressure drops and improve overall performance. Place electric-driven compressors and high-air compressors in a centralized area where the air can be evenly distributed to all connected tools without losing pressure over long distances.
For settings that use a 12L air compressor, keeping it closer to the point of use is advantageous to avoid loss of pressure due to long hose lengths. Shorter hoses and pipes reduce pressure drop, allowing tools to perform effectively with less strain on the compressor. Additionally, choosing hose materials that have less friction loss can further improve efficiency.
5. Optimize Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency is an important factor when running compressors in high-demand environments. Electric-driven compressors are generally more efficient than fuel-powered models, but further energy savings can be achieved by implementing certain practices. For example, using automatic shut-off controls can reduce unnecessary run-time, which is especially useful for electric-driven compressors. In periods of low demand, this feature conserves power and less wear.
For high air compressors, consider using variable speed drives (VSDs) if the compressor supports them. VSDs allow the motor to adjust its speed based on air demand, reducing energy consumption during periods of lower activity. Similarly, a 12L air compressor can benefit from a similar approach by utilizing pressure controls that turn the compressor off when the desired pressure is reached, and restart it when necessary.
Insulating pipes and hoses can also play a significant role in less energy loss. Insulation helps maintain air temperature, thereby reducing the compressor’s workload to achieve and maintain the desired pressure levels. Simple changes like this can advance to significant energy savings over time.
6. Ensure Proper Ventilation and Temperature Control
High-demand settings, especially in industrial or manufacturing contexts, often generate heat. Since electric-driven compressors are sensitive to temperature, ensuring proper ventilation can prevent overheating and extend compressor life. Place compressors in well-ventilated areas and avoid placing them near other heat-generating equipment.
When operating a high-air compressor, if the room temperature is controlled, the compressor runs more efficiently and is less likely to overheat. Proper ventilation is also necessary for smaller compressors, like the 12L air compressor, as these models can quickly overheat if overused without adequate airflow. Implementing a cooling system, such as a fan or air conditioning, in compressor rooms can also aid in temperature regulation.
7. Train Operators and Implement Standardized Procedures
Lastly, proper training is essential to ensure that air compressors are used efficiently. Operators should be familiar with the correct procedures for each type of compressor, such as electric-driven compressors, high air compressors, and 12L air compressors, to avoid improper handling that can advance to breakdowns or subpar performance. By implementing standard operating procedures (SOPs), you can ensure consistency in the way compressors are handled, inspected, and maintained.